In a world where digital currencies are taking over like a cat video on the internet, understanding blockchain is no longer just for tech gurus. It’s the backbone of cryptocurrencies and a game-changer for industries from finance to supply chain. If you’ve ever wondered how Bitcoin works or why everyone’s suddenly obsessed with NFTs, this blockchain basics tutorial is your golden ticket.
Blockchain Basics Tutorial
Blockchain technology serves as the backbone of various digital currencies and innovative applications across multiple sectors. Grasping its fundamentals enhances comprehension of its potential and impact.
What Is Blockchain?
Blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions across numerous computers. Each transaction, commonly called a block, connects to preceding blocks, creating a secure chain. This structure prevents data alteration and ensures transparency. Decentralization reduces reliance on a single authority, promoting trust in the system. Peer-to-peer networks facilitate direct transactions without intermediaries, streamlining processes. Popular cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum exemplify blockchain’s application in real-world scenarios, demonstrating its innovative capabilities.
Key Features of Blockchain
Blockchain boasts several key features that enhance its appeal. Security remains paramount, as cryptographic techniques protect data. Transparency enables all participants to verify transactions, fostering accountability. Immutability ensures once recorded, data cannot be altered, enhancing reliability. Additionally, decentralization distributes control across participants, minimizing risks associated with single points of failure. Scalability allows improvements in transaction throughput as technology evolves. Together, these features empower users with a robust framework for secure and efficient transactions.
Types of Blockchains
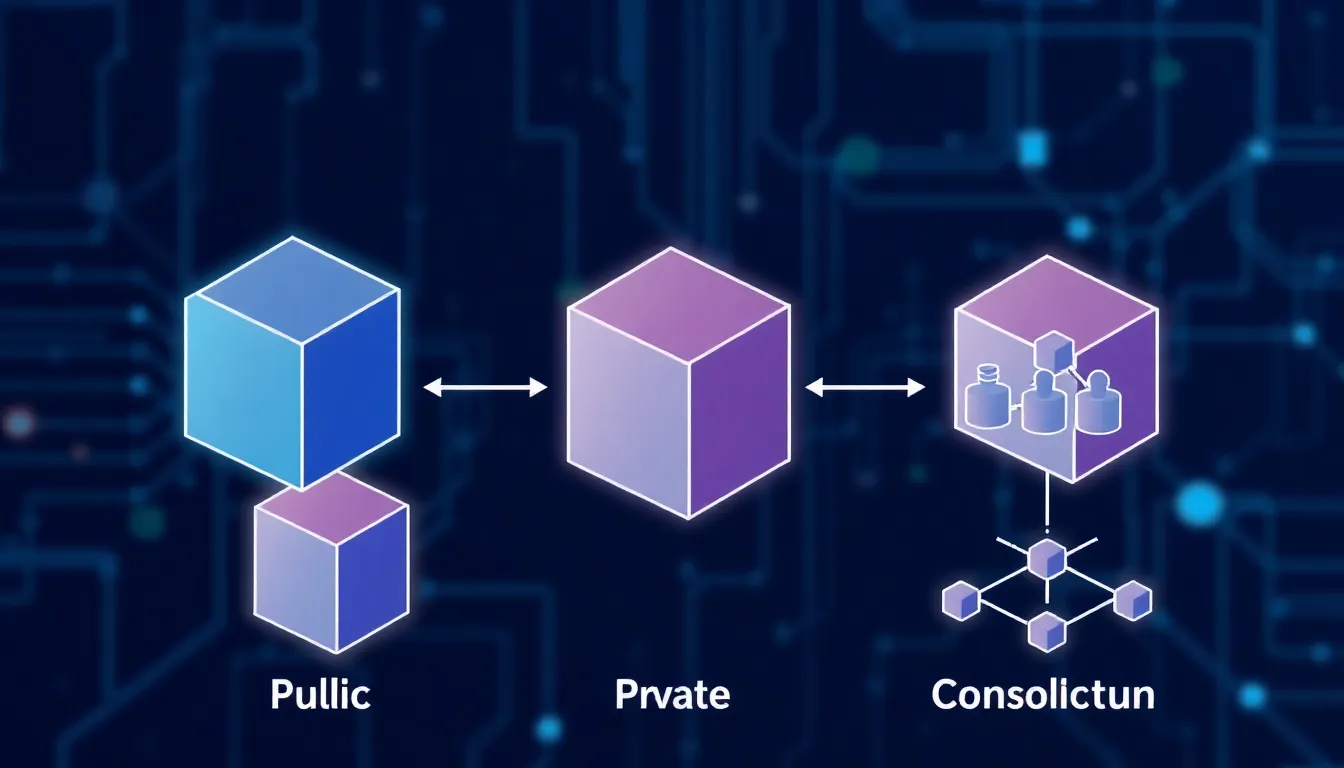
Different types of blockchains exist, each serving unique purposes. Understanding these types helps in grasping the overall functionality of blockchain technology.
Public vs. Private Blockchains
Public blockchains allow unrestricted access, meaning anyone can participate in transactions and contribute to the network. These networks operate on a decentralized model, promoting transparency and community engagement. Examples of public blockchains include Bitcoin and Ethereum. In contrast, private blockchains restrict access to select participants, providing enhanced privacy and control. Businesses often prefer private blockchains for sensitive data management. They often utilize consensus mechanisms like proof of authority rather than proof of work, improving efficiency while maintaining security.
Consortium Blockchains
Consortium blockchains operate through a collaborative approach, involving multiple organizations. These blockchains allow a group of pre-selected nodes to validate transactions, creating a balance between privacy and decentralization. Industries such as banking and supply chain management often adopt consortium blockchains for shared databases. Participants gain the ability to maintain control over their data while benefiting from the security of a blockchain structure. A notable example is the R3 Corda platform, which facilitates secure financial transactions among banks and financial institutions.
How Blockchain Works
Blockchain functions through a decentralized network that records transactions in a secure and transparent manner. Each transaction is grouped with others into blocks, creating a chain that digital ledgers maintain across multiple computers.
The Role of Nodes
Nodes play a crucial role in the blockchain ecosystem. Each node participates in the verification of transactions, helping to maintain the integrity of the entire network. Some nodes function as full nodes, storing complete copies of the blockchain, while others operate as light nodes, maintaining only essential information. Full nodes verify blocks after mining, ensuring all transactions conform to the rules. Additionally, nodes work collaboratively to propagate new transactions and blocks across the network, promoting decentralization and resilience against attacks.
Consensus Mechanisms
Consensus mechanisms are essential for verifying and validating transactions within a blockchain network. Various types exist, such as Proof of Work and Proof of Stake, each catering to different needs. Proof of Work requires significant computational power to solve complex mathematical problems, which secures the network. In contrast, Proof of Stake relies on the amount of cryptocurrency held by a participant to determine their ability to validate transactions. These mechanisms ensure agreement among nodes, preventing fraud and maintaining a consistent and secure blockchain environment.
Use Cases of Blockchain
Blockchain technology has numerous applications across different industries. Some notable use cases include cryptocurrency, supply chain management, and healthcare applications.
Cryptocurrency
Cryptocurrencies represent a significant use case for blockchain technology. Bitcoin and Ethereum exemplify how decentralized digital currencies function. Transactions occur securely through the blockchain, minimizing the risk of fraud. Users benefit from lower transaction fees compared to traditional banking methods. Market participants enjoy 24/7 trading availability, enabling real-time transactions across the globe. As adoption grows, cryptocurrencies continue to redefine the financial landscape.
Supply Chain Management
Blockchain enhances transparency and efficiency in supply chain management. It allows all stakeholders to track products from origin to destination with immutable records. Companies can verify the authenticity and quality of goods through real-time tracking. This technology reduces delays and disputes, streamlining processes. Businesses increasingly adopt blockchain for improved accountability among suppliers and partners. As a result, consumers gain confidence in product provenance.
Healthcare Applications
In healthcare, blockchain simplifies data management and sharing. Medical records stored on a blockchain provide patients with secure, accessible information. Healthcare providers can efficiently exchange patient data while maintaining privacy. The technology also aids in tracking drug supply chains, ensuring that medications are authentic and safe. With blockchain’s help, researchers can access reliable data for clinical studies and trials. Ultimately, patients and providers benefit from enhanced data integrity and security.
Getting Started with Blockchain
Understanding blockchain fundamentals involves using appropriate tools and resources. Beginners can explore various software solutions that facilitate blockchain development and experimentation.
Basic Tools and Software
Developers utilize tools like Ganache for creating personal Ethereum blockchains. This software lets users test smart contracts effortlessly. Truffle Suite serves as another powerful framework for building decentralized applications. It simplifies the process of managing smart contracts and network configurations. For real-time data interaction, tools such as Metamask connect users to Ethereum networks via a browser. This wallet also manages identities and transactions seamlessly. Remix IDE provides an integrated development environment for writing, debugging, and deploying smart contracts directly in a web browser.
Learning Resources for Beginners
Numerous online resources cater to blockchain novices. Coursera offers comprehensive courses covering blockchain basics, cryptocurrency knowledge, and smart contract development. Engaging video content is available on platforms like YouTube, where experts discuss practical implementations and trends in blockchain technology. Books such as “Mastering Bitcoin” and “The Basics of Bitcoins and Blockchains” provide in-depth insights for those interested in a thorough theoretical foundation. Community-driven forums like Stack Exchange encourage interaction, allowing users to ask questions and share knowledge. Online workshops and meetups foster networking and hands-on experiences, deepening understanding of real-world applications.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology is revolutionizing the way industries operate by providing secure and transparent solutions. Its decentralized nature ensures that transactions are immutable and verifiable, fostering trust among users. As more sectors recognize its potential, the demand for blockchain expertise continues to grow.
For those eager to dive deeper into this transformative technology, numerous resources and tools are available to aid learning and development. Embracing blockchain not only opens doors to innovative applications but also positions individuals and organizations at the forefront of the digital economy. Exploring its fundamentals today could lead to significant opportunities in the future.